Lint
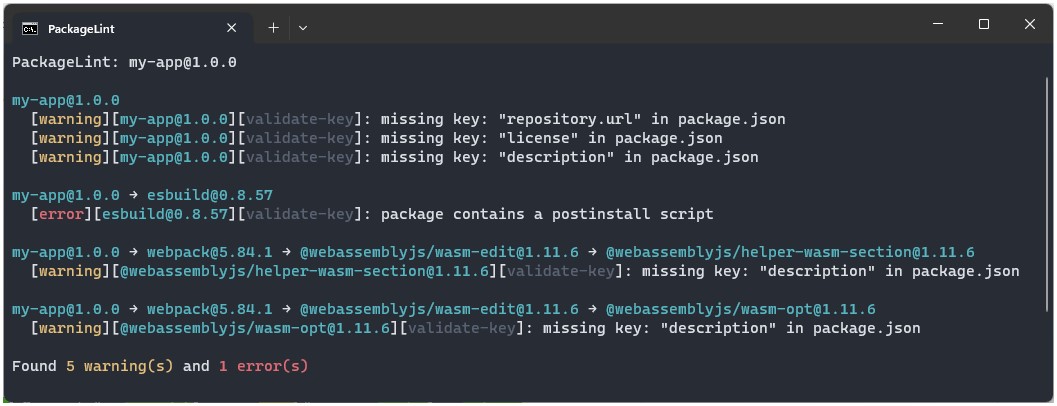
Introduction
The lint option lets you define and run checks on the dependency tree.
If an error is encountered, the lint process will exit with a non-zero status code.
Config File
The checks are defined in a config file that needs to be passed to the lint command. This file can be a JavaScript or a TypeScript file.
A sample config file in TypeScript could look like this:
const config = {
rules: [
// checks go here
[
"warning", // "warning" | "error"
{
name: `sample-check`,
check: (pkg: any) => {
const description = pkg.getData("description");
if (!description) return `No description found!`;
}
}
]
]
};
export default config;
This will surface all dependencies that don't contain a description as a warning.
For a more in depth explanation of how to write checks, please see this guide.
Options
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
lintFile | Path to the config file that contains the checks. |
--package | Package to run the checks on. Defaults to the latest version if no version is provided. |
--folder | Path to a folder that contains a local package.json. |
--depth | Depth to evaluate. If omitted, it will traverse the whole dependency tree. |
Example Usages
Lint whole dependency tree of latest React version
pkga lint ./path/to/lintConfig.ts --package react
Lint React only with specific version
pkga lint ./path/to/lintConfig.ts --package react@16.10.2 --depth 0
Lint local project
pkga lint ./path/to/lintConfig.ts --folder ./path/to/project
Rules
Currently, there is only one built in rule: the Validate Key rule. This rule allows you to check for the existence of certain keys in the package.json. Additionally, a custom validator can be provided for more sophisticated checks.
To write custom rules, please see this guide.